Definition
- Image Classification: 输入图片, 输出图中目标物体的类别.
- Object Localization: 输入图片, 输出图中物体的 bounding box.
- Object Detection: 输入图片, 输出图中物体的 bounding box 和类别.
R-CNN Model Family
采用region proposal methods, 首先生成潜在的bounding boxes, 然后采用分类器
识别这些bounding boxes区域. 最后通过post-processing来去除重复bounding boxes来进行优化.
这类方法流程复杂, 存在速度慢和训练困难的问题.
R-CNN
R-CNN 由三个部分组成:
- Region Proposal: Generate and extract category independent region proposals.
- Feature Extractor: Extract feature from each candidate region.
- Classifier: Classify features as one of the known class.
The feature extractor used by the model was the AlexNet deep CNN that won the ILSVRC-2012 image classification competition. The output of the CNN was a 4,096 element vector that describes the contents of the image that is fed to a linear SVM for classification, specifically one SVM is trained for each known class. 问题是运行很慢, test阶段CNN要从约2000个proposed region上提取特征.
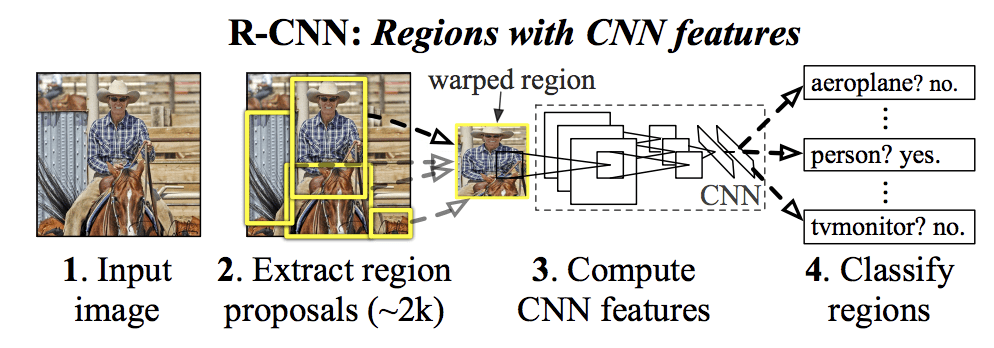
Fast R-CNN
提出了R-CNN的三个限制:
- Training is a multi-stage pipeline.
- Training is expensive in space and time.
- Object detection is slow.
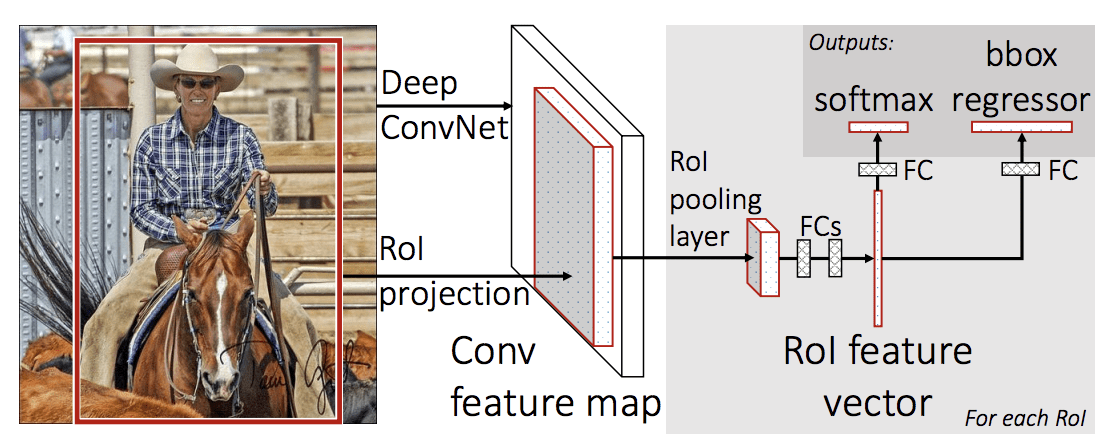
Fast R-CNN只训练一个模型去学习物体位置和分类, 而不是一个pipeline, 输入是一个region proposal的集合, 经过deep CNN, 进行特征提取. CNN的结尾是 Region of Interest Pooling Layer (ROI Pooling), 针对输入的candidate 进行特征提取. CNN的输出送入一个FC, 得到两个输出, 一个用于softmax layer预测类别, 另一个用于regression用于生成bounding box.
这个过程针对每一个region of interest进行循环.
Faster R-CNN
由两部分组成:
- Region Proposal Network: Convolutional neural network for proposing regions and the type of object to consider in the region.
- Fast R-CNN: Convolutional neural network for extracting features from the proposed regions and outputting the bounding box and class labels.
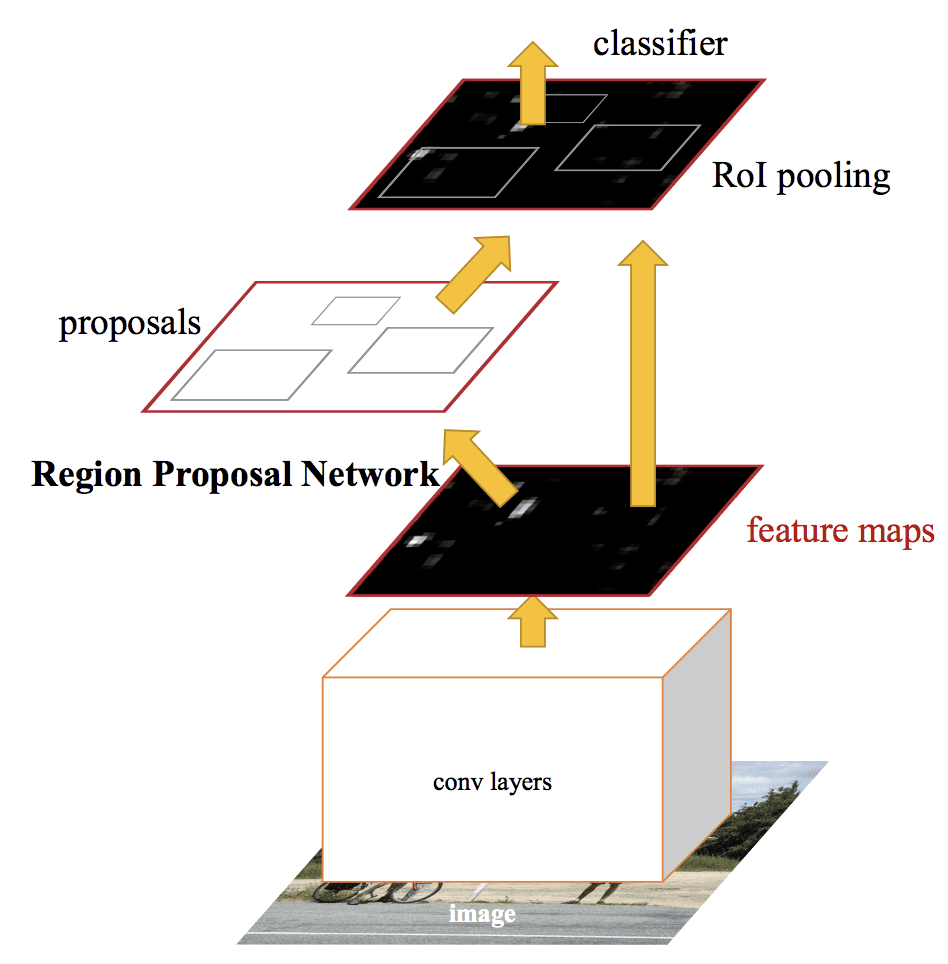
RPN网络接受CNN的输出, feature map送入一个小型网络得到许多region proposals, 每个对应一个分类. Region proposals是bounding boxes, 或者说anchor boxes, 后续优化. Class prediction is binary, indicating the presence of an object, or not, so-called “objectness” of the proposed region.
YOLO Model Family
YOLO
训练单独一个神经网络, 端到端, 接受一个图片直接预测bounding box. 准确率不高但是速度快.
YOLO首先将图像分为 $$S\times S$$ 的格子 (grid cell). 如果一个目标的中心落入格子, 该格子就负责检测该目标. (即使一个对象跨越多个网格, 它也只会被分配到其中点所在的单个网格. 可以通过增加更多网格来减少多个对象出现在同一网格单元中的几率.)
每一个格子 (grid cell) 预测bounding boxes(B)和该boxes的置信值(confidence score). 置信值代表box包含一个目标的置信度. 然后, 我们定义置信值为 $$Pr(Object)*IOU^{truth}_{pred}$$ . 如果没有目标, 置信值为零. 另外, 我们希望预测的置信值和ground truth的intersection over union (IOU)相同.
每一个bounding box包含5个值: $$x, y, w, h$$ 和confidence. $$(x, y)$$ 代表与格子相关的box的中心. $$(w, h)$$ 为与全图信息相关的box的宽和高. confidence代表预测boxes的IOU和gound truth. (IOU = 交叉面积/联合的面积)
每个格子(grid cell)预测条件概率值C $$Pr(Class_i|Object)$$ , 概率值C代表了格子包含一个目标的概率, 每一格子只预测一类概率. 在测试时, 每个box通过类别概率和box置信度相乘来得到特定类别置信分数: $$Pr(Class_i|Object)*Pr(Object)*IOU^{truth}{pred} = Pr(Class_i)*IOU^{truth}{pred}$$
这个分数代表该类别出现在box中的概率和box和目标的合适度. 例子讲解
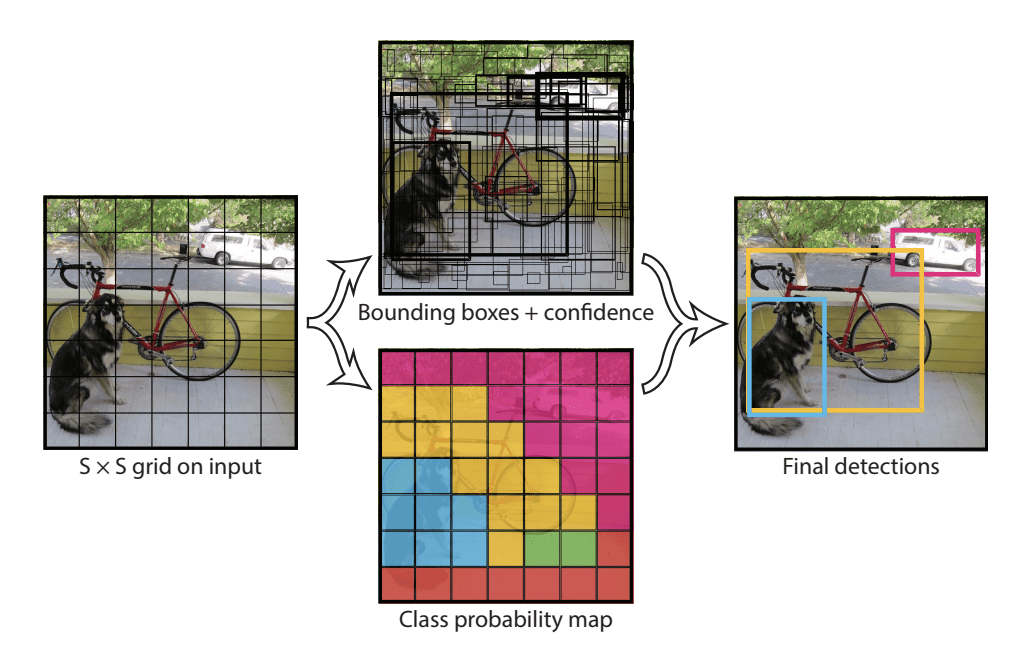
当一个目标不止一次被识别, 非极大值抑制可以显着提高YOLO的效果.
YOLO相对于传统方法有如下有优点:
- 非常快. YOLO预测流程简单, 速度很快. 我们的基础版在Titan X GPU上可以达到45帧/s; 快速版可以达到150帧/s. 因此, YOLO可以实现实时检测.
- YOLO采用全图信息来进行预测. 与滑动窗口方法和region proposal-based方法不同, YOLO在训练和预测过程中可以利用全图信息. Fast R-CNN检测方法会错误的将背景中的斑块检测为目标, 原因在于Fast R-CNN在检测中无法看到全局图像. 相对于Fast R-CNN, YOLO背景预测错误率低一半.
- YOLO可以学习到目标的概括信息 (generalizable representation), 具有一定普适性. 我们采用自然图片训练YOLO, 然后采用艺术图像来预测. YOLO比其它目标检测方法 (DPM和R-CNN) 准确率高很多.
YOLOv2 (YOLO9000) and YOLOv3
YOLOv2 model makes use of anchor boxes, pre-defined bounding boxes with useful shapes and sizes that are tailored during training.
The choice of bounding boxes for the image is pre-processed using a k-means analysis on the training dataset.
重要的是, 更改了边界框的预测表示形式, 以允许较小的更改对预测产生较小的影响, 从而产生更稳定的模型. 不是直接预测位置和大小, 而是预测偏移量, 以相对于网格单元移动和重塑预定义的锚框, 并通过逻辑函数对其进行阻尼.
[YOLOF: You Only Look One-level Feature](CVPR2021: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.09460.pdf)
Problem: Address optimization problem by utilizing only one-level feature for detection. Two key components, Dilated Encoder and Uniform Matching are proposed and bring considerable improvements.
Performance: YOLOF achieves comparable results with its feature pyramids counterpart RetinaNet while being $$2. 5\times$$ faster. Without transformer layers, YOLOF can match the performance of DETR in a single-level feature manner with $$7\times$$ less training epochs.
SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
- 问题: RCNN系列为two-stage方法, 先预先回归一次边框, 再进行骨干网络训练, 所以精度更高, 但速度方面有待提升. YOLO为one-stage方法, 只做一次边框回归和打分, 速度快但对小目标效果差, 对尺寸敏感.
- 使用one-stage思想, 融入Faster R-CNN中的anchor思想, 做了特征分层提取并以此计算边框回归和分类操作, 因此可以适应多尺度目标的训练和检测任务. 在每个stage中根据feature map的大小按照固定的ratio和scale生成default boxes. 例如conv9的输出feature map为5*5, 每个点默认生成6个box, 因此一张feature map上有5*5*6=150个default boxes, 而后每个default box将生成(c+1+4)维的特征向量, 其中c是类别数, 1代表背景, 4是box的偏移和缩放尺度.
- SSD的backbone是VGG16, 将最后的fc6和fc7转化成conv6和conv7, 再在之后加上不同尺度的conv8, 9, 10, 11四个卷积网络层.
- 联合损失函数 $L(x,c,l,g) = \dfrac{1}{N}(L_{conf}(x,c) + \alpha L_{loc}(x,l,g))$, 其中$L_{conf}$代表分类误差, 使用softmax; $L_{loc}$代表回归误差, 采用smooth L1 loss.
- $L_{loc}(x,j,g) = \sum_{i\in Pos}^N\sum_{m\in{cx,cy,w,h}}x_{ij}^ksmooth_{L1}(l_i^m - \hat{g}_j^m)$
- $L_{conf}(x,c) = -\sum_{x\in Pos}x_{ij}^p\log(\hat{c}{i}^p) - \sum{i\in Neg}\log(\hat{c}i^0), where\ \hat{c}{i}^p = \dfrac{\exp(c_i^p)}{\sum_p\exp(c_i^p)}$
- 训练策略:
- 匹配策略: 第一步是根据最大的overlap将ground truth和default box进行匹配, 第二步是将default boxes与overlap大于某个阈值的fround truth进行匹配.
- Default Boxes生成器: $S_k = S_{min}+\dfrac{S_{max}-S_{min}}{m-1}(k-1), k\in[1,m], ratio: a_r\in{1,2,\dfrac{1}{2}, 3, \dfrac{1}{3}}$
- Hard Negative Mining: 根据confidence loss对所有box进行排序, 选取置信度误差较大的top-k作为负样本, 使得正负样本比例控制在1:3之内.
PS: 正负样本怎么用啊啊啊啊